Cooling Tower (CT) Principle ?
 |
| CoolingTower |
- To decrease the temperature of hot water entering the CT.
- Cooling by evaporation is the principle used.
- Heat transfer from Water to Air.
- High difference between Wet Bulb Temperature ( WBT ) and Dry Bulb Temperature ( DBT ) encourages more Heat Transfer ( HT ) between air and water inside the cooling tower. This is due to the fact that when WBT = DBT , air is fully saturated i.e 100% relative humidity (R.H) and no longer accepts water, thus no more HT.
- Thus more difference between WBT and DBT => low R.H. => greater capacity to hold water => effective lowering of water temperature.
- Final outlet water temperature will always be < WBT of entering air. ( suppose DBT = 30°C, WBT = 25°C find R.H from humidity chart, this implies the capacity of air to hold water i.e. hot water can maximum transfer heat till its drops to WBT of entering air )
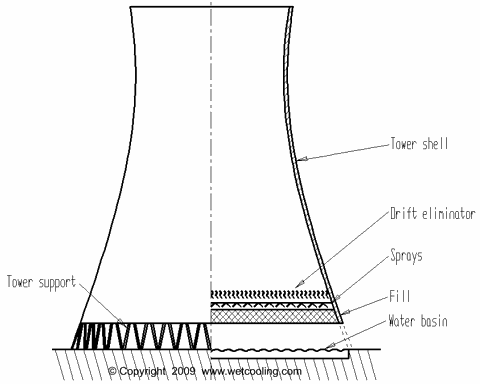
Working of CT ?
- Hot water from HE enters cooling tower
- It is sprinkled from top with the help of nozzles
- fills are used for better Heat Transfer between air and water.
- Normally water is brought down to room temperature and is collected in the concrete basin at the bottom.
- This water is re-used again and the same process follows.
- small amount of water gets evaporated during the entire process hence make up water is used .
Types of CT
1. Natural Draft ( Hyperbolic CT ) :
- ADVANTAGES : No fans, motors or gearboxes required, usually used for large quantity of water flow.
- DISADVANTAGE : Large space required
- uses the difference between ambient air temperature and the air inside tower.
- Hot air rises upwards and cooler air is drawn inside through bottom.
- Two types :
B) Counter Flow Natural Draft CT: Air is dawn up through the falling water. Fill is located inside.
2. Mechanical Draft CT
Requires large fans to force air (forced draft CT) or draw air (induced draft CT) through the CT.
FORCED DRAFT:
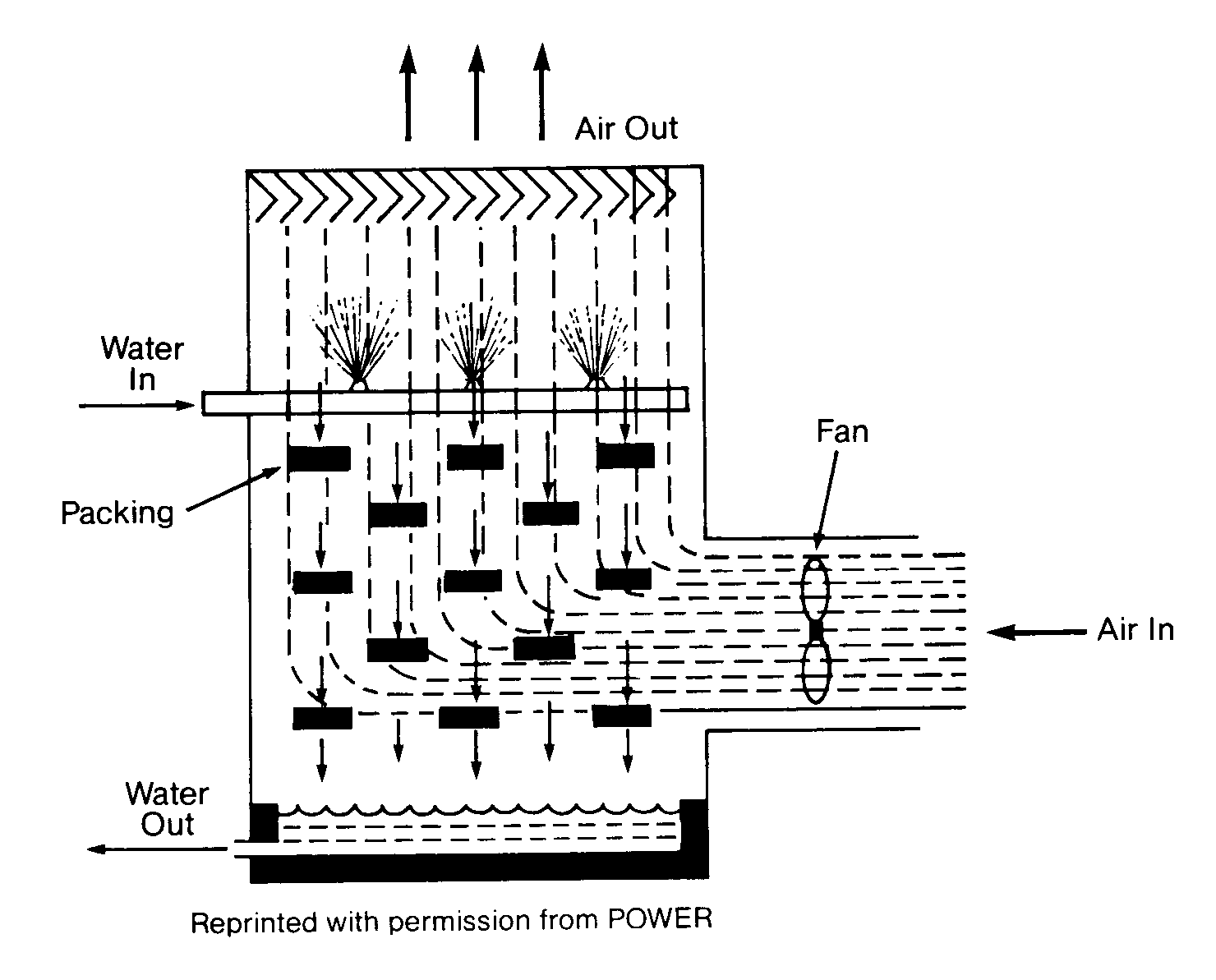
- can be of square or rectangle shaped only (natural draft are Bottle shaped ) because of large fan on the side.
- Entering velocity > exiting velocity, thus affecting the approach of CT. ( possibility of warm air getting sucked in blower, thus increasing the WBT of entering air ).
- cold water basin is covered , hence difficult to access.
- Fills are inaccessible (as seen in fig.)
- Forced draft requires more Horse power.
- Cannot be cross flow in nature Forced Draft CT
Merits :
- can be installed in confined space
- Able to work with high static pressure.
INDUCED DRAFT :
Merits :
- Less noise since fan is placed at the top of CT.
- Less re-circulation (since exiting velocity > entering velocity )
- Sprinkler water distribution system is used
- Can be both cross flow as well as counter flow in nature.
- Parts are easily accessible
Both types differ in fill arrangement and water -air flow
- Counter flow Induced Draft CT :
2. Cross flow Induced Draft CT:
- Air moves horizontally through the fill and water falls through gravity.
- No sprinkler can be used.
- Less efficient compared to counter flow ( ~ 25% )
- Difficult to clean at cold water basin due to limited access.
- Requires safety guidelines ( handrail, safety cage, service platform ) as per OSHA.
- maintenance is high comparatively.
- less initial cost. ( since counter flow is huge in size )
Terms Used in CT ?
1) Range : (HOT water entering) - (COLD water leaving tower)
2) Approach : Cold water leaving - wet bulb temperature of air.
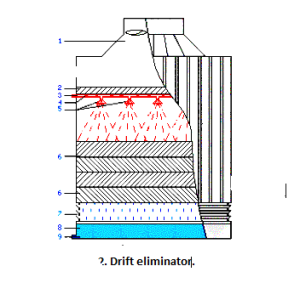
3) Drift eliminators : To avoid the water being carried away by the exhaust air, by using baffle like , drift eliminators through which air has to pass after passing through fills and spray tower.
4) Heat Load: heat to be removed from circulating water. Unit = Btu/hr
5) Ton : Evaporative cooling ton is 15,000 BTU's / hr & refrigeration ton is 12,000 BTU's / hr.
6) WBT : lowest temperature theoretically reached by water in CT. V. Imp parameter in CT.
7) Makeup : Amount of water added to compensate for evaporation loss in CT.
8) Bleed off : Maintains amount of dissolved impurities and solids by removing portion of circulating water.
9) Fills : For achieving more HT.
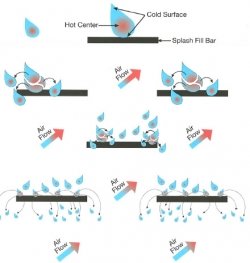
Types -
- used to increase HT between water and air by dividing water into fine droplets.
- Wooden and Plastic splash fill's are used.
- Wooden splash fills are prone to rot problems and hence they are used after applying a preservative over it.
- PVC splash fill's offers more HT and is preferred over wooden fills
- Honeycomb structure
- plastic generally used
- Preferred over splash due to high efficiency.
- Not preferred if the circulating water has considerable amount of solid, which will block the passageway.






GOOD JOB DONE
ReplyDeleteThank You !!!
ReplyDeleteKindly subscribe to my blog (at the top) to receive email when a new post is made.
Why wooden fills are used in CT??
ReplyDeletewooden fill's were brought to use since 1940's. Redwood has natural resistance to rot problems and hence was in great demand until 1960's, but its high cost and less availability forced to move to Fir wood ( which has no natural resistance to rot problem) and thus it had to be treated with water repellent preservative before being used as splash fill.
ReplyDeletePurpose is to form a film on the wood or block the wooden pores by using preservatives, so that rotting and microbial growth is avoided.
However, now-a-days high performance PVC are used which forms better droplets and allows scope for better heat transfer.
Thnk u sir...
ReplyDeleteHi Friends,
ReplyDeleteCooling towers come in many different shapes and sizes. They range from small two-ton factory assembled models to large field erected towers capable of rejecting thousands of BTU of heat. Although the shapes and sizes can vary, the principle of operation remains the same. Thanks a lot...
Heat Exchanger Fouling : Thanks for sharing the information.
ReplyDeleteGood work & Nice pictures.
ReplyDeleteI could read only first few para and found another fundamental error. You said Water outlet temperature < WBT of entering air. It is actually opposite.
Check out detailed analysis of cooling tower performance on my blog.
http://profmaster.blogspot.in
Thank You for the correction, I wonder why I couldn't find this mistake before publishing. I apologize for my error. I'll make the necessary changes.
ReplyDeleteThank's once again.
Impact fans regularly provide efficiencies of 15-40% over other makes in wet cooling applications like cooling tower. All of our fans installed worldwide are saving energy at the rate of 250MW. Our fans provide a less expensive and quick fix to reducing the auxiliary power consumption in a plant. The fact that the fans are made of FRP makes them extremely corrosion resistant and durable and suitable for years of use without replacement. In summer months, the advantages become even more apparent as the pitch of the blades can be increased to draw more air- something made possible by the high level of energy efficiency.
ReplyDelete