Cooling Tower (CT) Principle ?
 |
| CoolingTower |
- To decrease the temperature of hot water entering the CT.
- Cooling by evaporation is the principle used.
- Heat transfer from Water to Air.
- High difference between Wet Bulb Temperature ( WBT ) and Dry Bulb Temperature ( DBT ) encourages more Heat Transfer ( HT ) between air and water inside the cooling tower. This is due to the fact that when WBT = DBT , air is fully saturated i.e 100% relative humidity (R.H) and no longer accepts water, thus no more HT.
- Thus more difference between WBT and DBT => low R.H. => greater capacity to hold water => effective lowering of water temperature.
- Final outlet water temperature will always be < WBT of entering air. ( suppose DBT = 30°C, WBT = 25°C find R.H from humidity chart, this implies the capacity of air to hold water i.e. hot water can maximum transfer heat till its drops to WBT of entering air )
Working of CT ?
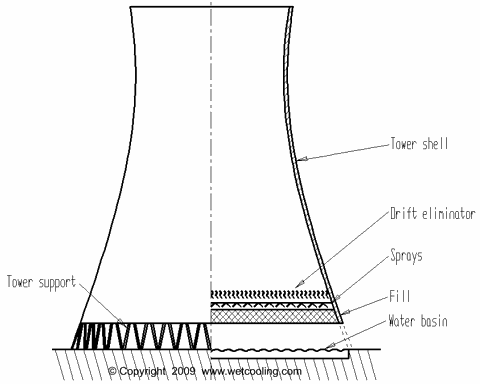
- Hot water from HE enters cooling tower
- It is sprinkled from top with the help of nozzles
- fills are used for better Heat Transfer between air and water.
- Normally water is brought down to room temperature and is collected in the concrete basin at the bottom.
- This water is re-used again and the same process follows.
- small amount of water gets evaporated during the entire process hence make up water is used .
Types of CT
1. Natural Draft ( Hyperbolic CT ) :
- ADVANTAGES : No fans, motors or gearboxes required, usually used for large quantity of water flow.
- DISADVANTAGE : Large space required
- uses the difference between ambient air temperature and the air inside tower.
- Hot air rises upwards and cooler air is drawn inside through bottom.
- Two types :
B) Counter Flow Natural Draft CT: Air is dawn up through the falling water. Fill is located inside.